Many times in business and life, we want to determine the value today of receiving a specific single amount at some time in the future. Essentially, present value is an effective way of comparing investment decisions or purchase decisions. If you expect to have $50,000 in your bank account 10 years from now, with the interest rate at 5%, you can figure out the amount that would be invested today to achieve this.
Present Value of a Growing Perpetuity (g = i) (t → ∞) and Continuous Compounding (m → ∞)
Calculating the Present Value of multiple cash flows is actually very similar to the single cash flow case. So let’s go ahead now and step things up just a little bit by considering the case with multiple cash flows. If we assume a discount rate of 6.5%, the discounted FCFs can be calculated using the “PV” Excel function. The core premise of the present value theory is based on the time value of money (TVM), which states that a dollar today is worth more than a dollar received in the future. The time value of money (TVM) principle, which states that a dollar received today is worth more than a dollar received on a future date. The present value is the amount you would need to invest now, at a known interest and compounding rate, so that you have a specific amount of money at a specific point in the future.
Other important present value calculations
- Using present value is a quick and easy way to assess the present and future value of an investment.
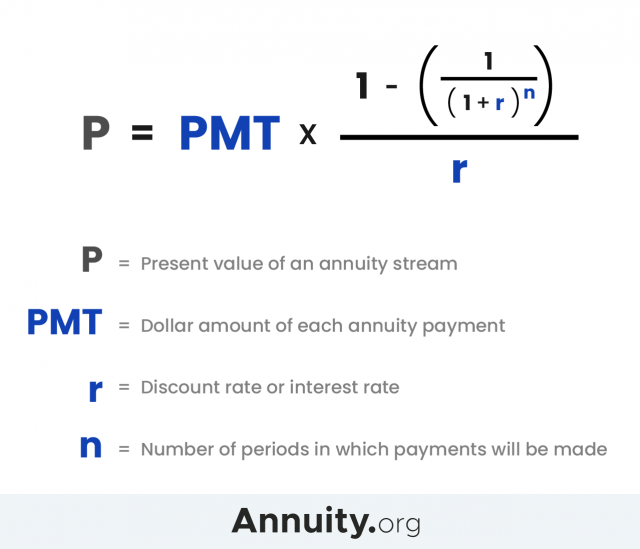
- The term present value formula refers to the application of the time value of money that discounts the future cash flow to arrive at its present-day value.
- Take your time to think about the equation and think about how it is actually a function of two things — future expectations and risk.
- PV helps investors determine what future cash flows will be worth today, allowing them to understand the value of an investment and thereby choose between different possible investments.
For example, if your payment for the PV formula is made monthly, then you’ll need to convert your annual interest rate to monthly by dividing by 12. Also, for NPER, which is the number of periods, if you’re collecting an annuity payment monthly for four years, the NPER is 12 times 4, or 48. The big difference between PV and NPV is that NPV takes into account the initial investment. The NPV formula for Excel uses the discount rate and a series of cash outflows and inflows. “Discounting” is the process of taking a future cash flow expressing it in present terms by “bringing it back” to the present day.
How do I distinguish between future value and present value problems?
Use this PVIF to find the present value of any future value with the same investment length and interest rate. Instead of a future value of $15,000, perhaps you want to find the present value of a future value of $20,000. Calculate the Present Value and Present Value Interest Factor (PVIF) for a future value return.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
The present value is calculated to be ($30,695.66) since you would need to put this amount into your account; it is considered to be a cash outflow, and so shows as a negative. If the future value is shown as an outflow, then Excel will show the present value as an inflow. what is a tax deduction And now that we know how to estimate the Present Value of multiple cash flows, we can think about what the Present Value formula actually looks like. The approach to discount these 3 cash flows is actually identical to the case of the single cash flow we saw earlier.
The Time Value of Money

Once these are filled, press “Calculate” to see the present value and the total interest accumulated over the period. The present value of an investment is the value today of a cash flow that comes in the future with a specific rate of return. If you find this topic interesting, you may also be interested in our future value calculator, or if you would like to calculate the rate of return, you can apply our discount rate calculator.
The Present Value is an incredibly important concept – it’s what approximately 70-80% of Finance is based on in one way or another. So it’s the value of something expressed in today’s terms or in present terms. We’re going to assume that you’re more or less alright, so let’s actually just think about that equation in a little more detail. We’re going to assume that you (at least roughly) know how to calculate the FV.
The default calculation above asks what is the present value of a future value amount of $15,000 invested for 3.5 years, compounded monthly at an annual interest rate of 5.25%. The current cash amount determined by subtracting interest to be earned over time from the future cash amount. It’s called the Rule of 72, which tells you the number of years it takes for your money to double at a given annual rate of return.
In the present value example, however, the interest rate is applied twice. This means that the future value problem involves compounding while present value problems involve discounting. The present value formula assumes that you are earning an expected forgone rate of return over a predetermined period of time. The term present value formula refers to the application of the time value of money that discounts the future cash flow to arrive at its present-day value. By using the present value formula, we can derive the value of money that can be used in the future. The present value (PV) calculates how much a future cash flow is worth today, whereas the future value is how much a current cash flow will be worth on a future date based on a growth rate assumption.
It is determined by discounting the future value by the estimated rate of return that the money could earn if invested. Present value calculations can be useful in investing and in strategic planning for businesses. The present values today will be less than if we simply added the sum of each future cash deposit in the future to determine their total.
